Mortgage Types in the USA
Mortgage Types in the USA, In the United States, there are several main types of mortgages, each catering to different financial situations and homeownership goals. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most common:
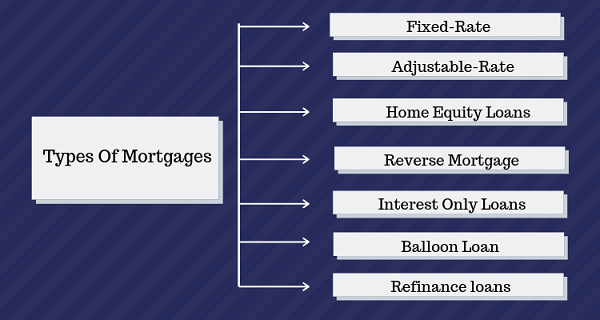
Navigating the Mortgage Maze: Loan Types in the USA
The American goal of owning a home frequently entails having to take out a mortgage. But with so many different kinds of loans available, picking the best one can be difficult. Below is a summary of several important mortgage choices available in the United States:
By Loan Source:
Conventional Mortgages:
Conventional mortgages, which are offered by private lenders and are not protected by government insurance, make up the bulk of mortgages in the United States. For these loans, you usually need a decent credit score (usually around 660) and a down payment (usually between 3% and 20% of the property value). Compared to government-backed options, conventional mortgages may be more flexible and have lower interest rates. Because of the stricter qualifying requirements, they are less accessible to those with weaker credit ratings or smaller down payments.
Lenders also check for a high credit score (often over 660) to make sure you can afford to return the loan. The benefit? Interest rates on conventional mortgages are frequently more affordable than those on government-insured loans. Lower monthly payments and possibly large savings throughout the loan are the results of this. The more stringent qualifying standards, however, may provide a challenge for many borrowers, especially those who are purchasing their first home and do not have a substantial down payment or a long credit history.
Government-Backed Mortgages:
Government-backed mortgages act as a safety blanket in the US housing market, enabling more people to become homeowners. Federal agencies like the Department of Veterans Affairs, the US Department of Agriculture, and the Federal Housing Administration support these options. With government backing, lenders can offer more permissive terms, especially when it comes to credit score and down payment. For instance, VA loans may not need a down payment for qualified veterans and active military personnel, while FHA loans may be accessible with a credit score as low as 580 and a 3.5% down payment. Mortgage Types in the USA.
Government-backed mortgages can have stricter qualification requirements, such as income ceilings or property location restrictions for USDA loans. They may also have slightly higher interest rates than typical loans due to the government’s involvement. Government-backed mortgages are necessary to promote homeownership and a healthy housing market despite these disadvantages, particularly for first-time buyers, veterans, and residents of rural areas.
By Interest Rate:
Fixed-Rate Mortgages:
Fixed-rate mortgages are the cornerstone of predictability and stability in the US housing market. With a fixed-rate mortgage, your locked-in interest rate at loan origination stays the same for the duration of the loan, which is typically 15 to 30 years. Homeowners will have a great deal of peace of mind knowing exactly how much their monthly mortgage payment will be for as long as the loan is in existence.
Also Read: mortgage calculator, loan calculator, mortgage rates, home loan calculator
This regularity makes it easier for homeowners to budget and plan financially by allowing them to put in a regular housing cost without having to worry about fluctuations. One major advantage of fixed-rate mortgages is the long-term security they offer, even if their initial interest rates are frequently slightly higher than those of adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs). In periods when interest rates are rising, this is particularly true for homeowners with fixed-rate mortgages, as they are shielded from future increases, preserving their monthly payments and overall financial stability. mortgage calculator, loan calculator, mortgage rates, home loan calculator.
Adjustable-Rate Mortgages (ARMs):
Adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) are a tempting option for some American borrowers, especially those looking for a lower initial point of entry into housing. The interest rates on adjustable mortgages (ARMs) are subject to regular fluctuations, typically following an initial three, five, or seven-year period. Because this initial interest rate is often lower than a fixed-rate mortgage, your monthly payments throughout the first years of your loan could be lower. For first-time purchasers or those wishing to free up cash flow in the early stages of homeownership, this might be a helpful benefit. Mortgage Types in the USA.
Still, there’s a risk involved with ARMs’ changeable nature. Following the completion of the promotional term, the interest rate will fluctuate by a financial index—typically the Prime Rate or LIBOR. Your ARM’s interest rate will probably increase in tandem with market rates, which will result in greater monthly payments. If you don’t give this considerable thought, it might put a strain on your finances and throw off your financial strategy. Because of this, borrowers who expect short-term ownership or who are at ease with probable interest rate changes are the greatest candidates for ARMs. Before choosing an ARM in the USA, careful planning and a clear understanding of your risk tolerance are essential.
Other Mortgage Types:
Jumbo Loan: If you want to finance a luxury property in the United States that exceeds the Federal Housing Finance Agency’s (FHFA) conforming loan limits, you may be able to do so with a jumbo loan. Jumbo loans, despite their stricter standards, are designed specifically for this wealthy market. Be prepared to pay a greater down payment (often more than 20%), have a higher credit score, and maybe pay slightly more in interest as compared to standard conforming loans.
Home Equity Loan/Line of Credit (HELOC): Homeowners can access the equity they have accrued in their house through a home equity loan or line of credit (HELOC). A HELOC works like a credit card that is secured by your house, as opposed to a standard mortgage where you get paid in full upfront. Up to a certain credit limit, you can borrow money as needed; you simply pay back interest on the amount borrowed. This flexibility can help pay for schooling, debt consolidation, or home improvements, but keep in mind that you are borrowing against the value of your house, so making your loan payments on time will help you avoid the risk of foreclosure.
Choosing the Right Mortgage:
Your credit score, ability to make a down payment, risk tolerance, and financial status all play a role in selecting the ideal mortgage for you. When making your choice, take into account variables including interest rates, loan terms, and any upfront charges. You can investigate your alternatives and choose the one that best suits your needs by speaking with a mortgage lender.
mortgage calculator, loan calculator, mortgage rates, home loan calculator